Describe the Cell Cycle Using at Least Three Sentences
After cells divide they enter the longest phase of the cell cycle and of three. The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events.

The Cell Cycle Biology For Majors I
Cancer is basically a disease of uncontrolled cell division.
. It is important to organisms in different ways but overall it allows them to survive. The stages of the cell cycle Complete the following sentences to describe the stages of the cel cycle Choices may be used more than once. Cell biology is the study of cells their physiology structure and life cycle.
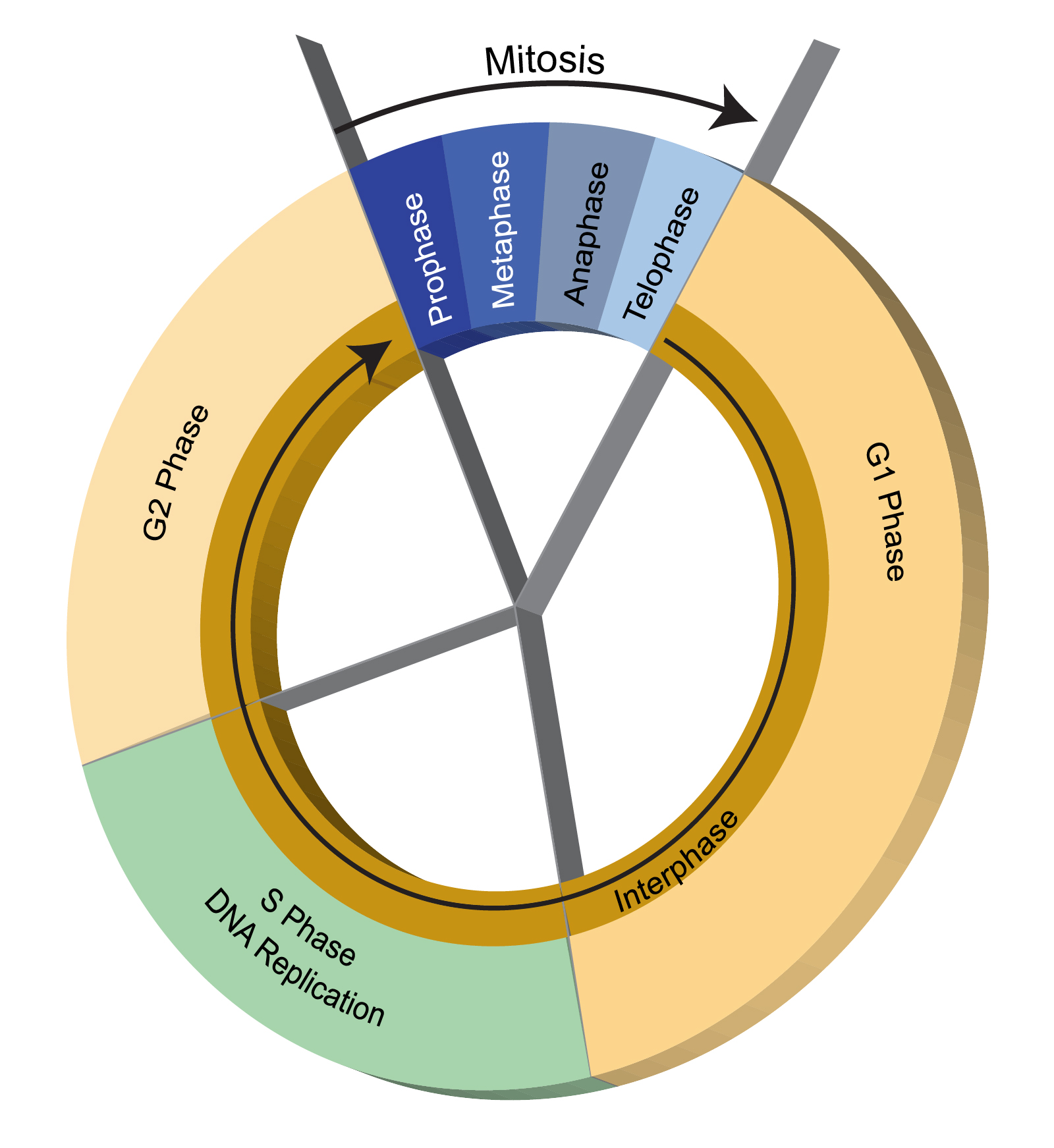
A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase and during this time it grows replicates its chromosomes and prepares for cell division. These events include the duplication of its DNA and some of its organelles and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. Interphase is divided into G 1 S and G 2 phases.
G1 phase S phase synthesis G2 phase collectively known as interphase and M phase mitosis. G 1 gap1 phase 2. During M phase or mitosis the cell divides.
Human cells exhibit typical eukaryotic cell cycle and take around 24 hours to. The events in this stage of the cell cycle leading to cell division are prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. The division cycle of most cells consists of four coordinated processes.
These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. When the new cell comes into operation and becomes the head of the battery the first or tail cell is thrown out and number two becomes the tail cell and so the rounds are repeated. G1is the gap between M phase and S phase while G2is the gap between S phase and M phase.
Teach your students about cell biology using these classroom resources. For example inhibitors of the cell cycle keep cells from dividing when conditions arent right so too little activity of these inhibitors can promote cancer. In cells with nuclei the cell cycle is divided into.
Cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. This is the first stage of the cell cycle and occurs before mitosis. The cell then leaves interphase undergoes mitosis and completes its division.
The G 1 phase is set in immediately after the cell division. The mitotic phase begins with karyokinesis mitosis which consists of five stages. Learn about the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
The cell cycle is the replication and reproduction of cells whether in eukaryotes or prokaryotes. In M phase the more. Its development and progression are usually linked to a series of changes in the activity of cell cycle regulators.
The cell grows continuously in interphase which consists of three phases. One cell is always being emptied and one filled or charged with slices and heated up the latter becoming the head of the battery as soon as it is ready. A cell cycle is a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides.
The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. The phases of the cell cycle. DNA replication is confined to S phase.
The stages G1 S and G2 make up interphase which accounts for the span between. A critical step in the cell cycle is the proper attachment of chromosomes to the mitotic spindle during metaphase. The cell cycle is composed of interphase G₁ S and G₂ phases followed by the mitotic phase mitosis and cytokinesis and G₀ phase.
The spindle fibers pull apart with a pair of chromatids and move towards opposite sides of the cell. During this phase the cell grows makes a copy of its DNA the chromosomes are copied and prepares to divide into two cells. In bacteria cell growth and DNA replication take place throughout most of the cell cycle and duplicated chromosomes are distributed to daughter cells in association with the plasma.
In rapidly dividing human cells with a 24-hour cell cycle the G 1 phase lasts approximately nine hours the S phase lasts 10 hours the G 2 phase lasts about four and one-half hours and the M phase lasts approximately one-half hour. S synthesis phase 3. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages.
The following points highlight the four major phases of the cell cycle. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth DNA replication and division that produce two genetically identical cells. The two structures that are being copied are cylindrical in shape and are called centrioles.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. For eukaryotes consider an animal such as a cat if a cat were to have a. The two major phases of the cell cycle are interphase and M phase.
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication replicationThe cell cycle consists of four distinct phases. During one portion of interphase the cells DNA is copied. Cell cycle the ordered sequence of events that occur in a cell in preparation for cell division.
M mitosis and cytokinesis. All living organisms are composed of cells from just one unicellular to many trillions multicellular. In early embryos of fruit flies the cell cycle is completed in about eight minutes.
The microtubules and chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle fibers. The chromosomes duplicate and become coiled. If a cell that is in G1 is not biologically ready to continue on to S phase either because it has not reached a sufficient size or does not have the appropriate cellular environment what does it do.
Explore cell repair and understand how the G0 phase relates to. For prokaryotes the cell cycle called Binary Fission allows for them to live on by dividing into two new daughter cells. Phases of Cell Cycle.
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. In eukaryotes the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period called interphase. The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size gap 1 or G1 stage copies its DNA synthesis or S stage prepares to divide gap 2 or G2 stage and divides mitosis or M stage.
Then place the sentences in ch order beginning with a freshly divided cell Drag the text blocks below Into their correct order. It is characterised by a change in the chromosome from the condensed mitotic state to the more extended interphase. The bodys cells spend time resting in a phase known as G0.
During meiosis cells exit the vegetative cell cycle and enter a linear divisional and differentiation pathway. G 2 gap 2 phase 4. Cell growth DNA replication distribution of the duplicated chromosomes to daughter cells and cell division.

Cell Cycle Definition Phases Examples Regulation Biology Dictionary

Comments
Post a Comment